What's new?
This page shows features that have landed to kepler.gl in major versions. For a complete list of changes to kepler.gl including each minor version, please visit the full change log.
3.2
Released August 21st, 2025
Raster Tile Layer
The new Raster Tile layer enables visualization of satellite and aerial imagery from raster PMTiles and Cloud-Optimized GeoTIFFs (via STAC). Use it to bring large imagery datasets into kepler.gl without dedicated tile infrastructure for raster PMTiles, or connect through a compatible raster tile server for COGs and elevation.
WMS Layer
The new WMS layer adds support for rendering imagery and map tiles from OGC Web Map Service endpoints, allowing you to integrate enterprise or public WMS sources directly in kepler.gl.
AI Assistant
Generate idea buttons from the LLM to speed up workflows.
More reliable local model connectivity (fix for Ollama connection issues).
Configuration migrated to TypeScript for better npm consumption.
More Bug Fixes and Improvements
Fit-to-bounds: fix initial basemap and deck projections mismatch.
Aggregation layers: fixes for custom color scales.
Vector tiles: regression fixes for field extraction and setup flow.
Image export: fixes when effects are enabled.
Loading indicator: behavior and visibility improvements.
DuckDB: fix importing files with spaces in column names.
For the complete list of commits, see the full change log.
3.1.1
Released March 10th, 2025
DuckDB
The DuckDB integration has been updated in response to feedback and requests, speeding up workflows for projects with local data. Notable changes include:
Users can now drag and drop files directly in kepler.gl to create a DuckDB table.
The schema panel now always updates when running a query.
Improved handling of DuckDB column types.
Vector Tiles
The Vector Tile layer has received a number of optimizations, bug fixes, and quality-of-life improvements. Notable changes include:
For older tilesets without fields in the metadata file, kepler.gl now attempts to retrieve fields from the tile data.
Automatically center the map to the tileset bounds.
Fix for UI freezes during initial Tileset setup.
More Bug Fixes
A number of bug fixes have been deployed in response to community feedback. The most notable bug fixes are listed below, but you can view a full list of changes in the full change log.
Fix for geocoder coordinates, allowing users to enter coordinates directly.
Fix for icon layers at higher zoom levels—icons now remain the same size.
Fix for a broken section of the Icon Layer UI.
Ensure the RangeBrush updates when the slider range changes.
Transform binary buffers to hex WKB when saving to JSON/HTML maps.
Improved logic for changing layer types.
Support arrow text labels from non-string vector sources.
Export GeoArrow columns to CSV as GeoJSON.
Restore support for string WKB data; save binary WKB as hex WKB.
AI Assistant now sends messages to 127.0.0.1 instead of a remote Ollama URL.
Fix for disappearing heatmaps when rendering black or duplicate colors.
Fix for point column suggestions not working.
Fix for crashes in GeoJSON and Trip layers when no data is present.
Fix for the "Save Map" action when using the FSQ provider (overwrite logic).
FSQ storage provider now prompts for login instead of auto-login after logout.
3.1
Released January 29th, 2025
Vector Tiles
The new Vector Tile layer allows the map to dynamically retrieve data based on the user's viewport and zoom level. This initial release supports both Mapbox Vector Tiles and PMTiles.
By leveraging the efficiency of vector tiles, users can visualize complex, large-scale datasets without compromising performance, making it easier to explore and analyze geospatial data.
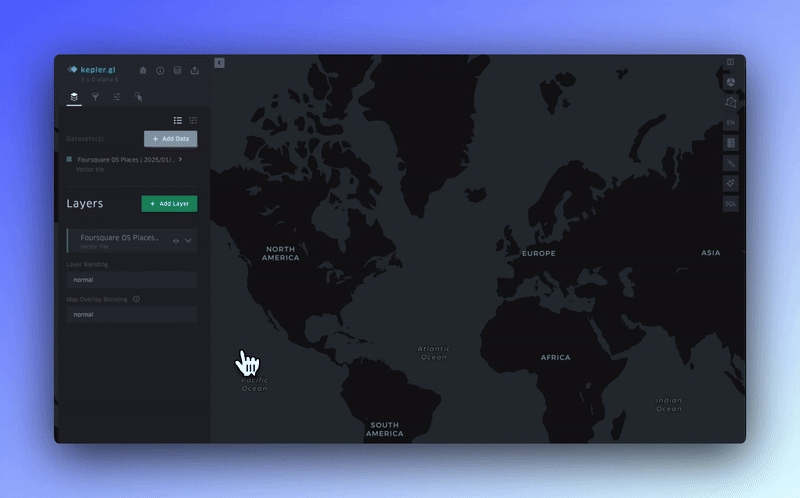
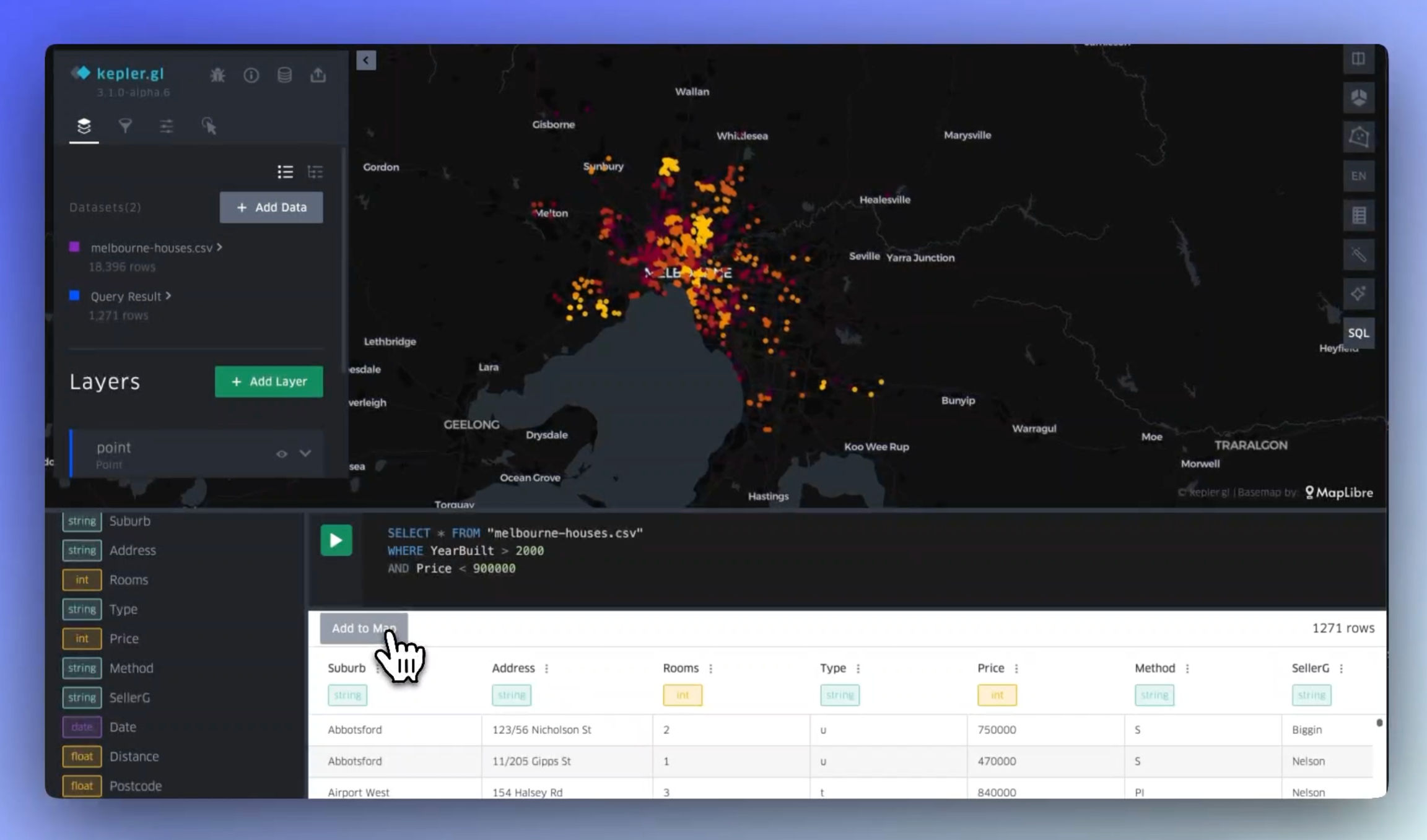
DuckDB Support & SQL Explorer
Leverage DuckDB directly within kepler.gl your geospatial projects with big data. Write and execute SQL queries to perform custom analyses, visualizing the results on your map.
DuckDB enables in-browser data processing, allowing you to work with large datasets without the need for external infrastructure.
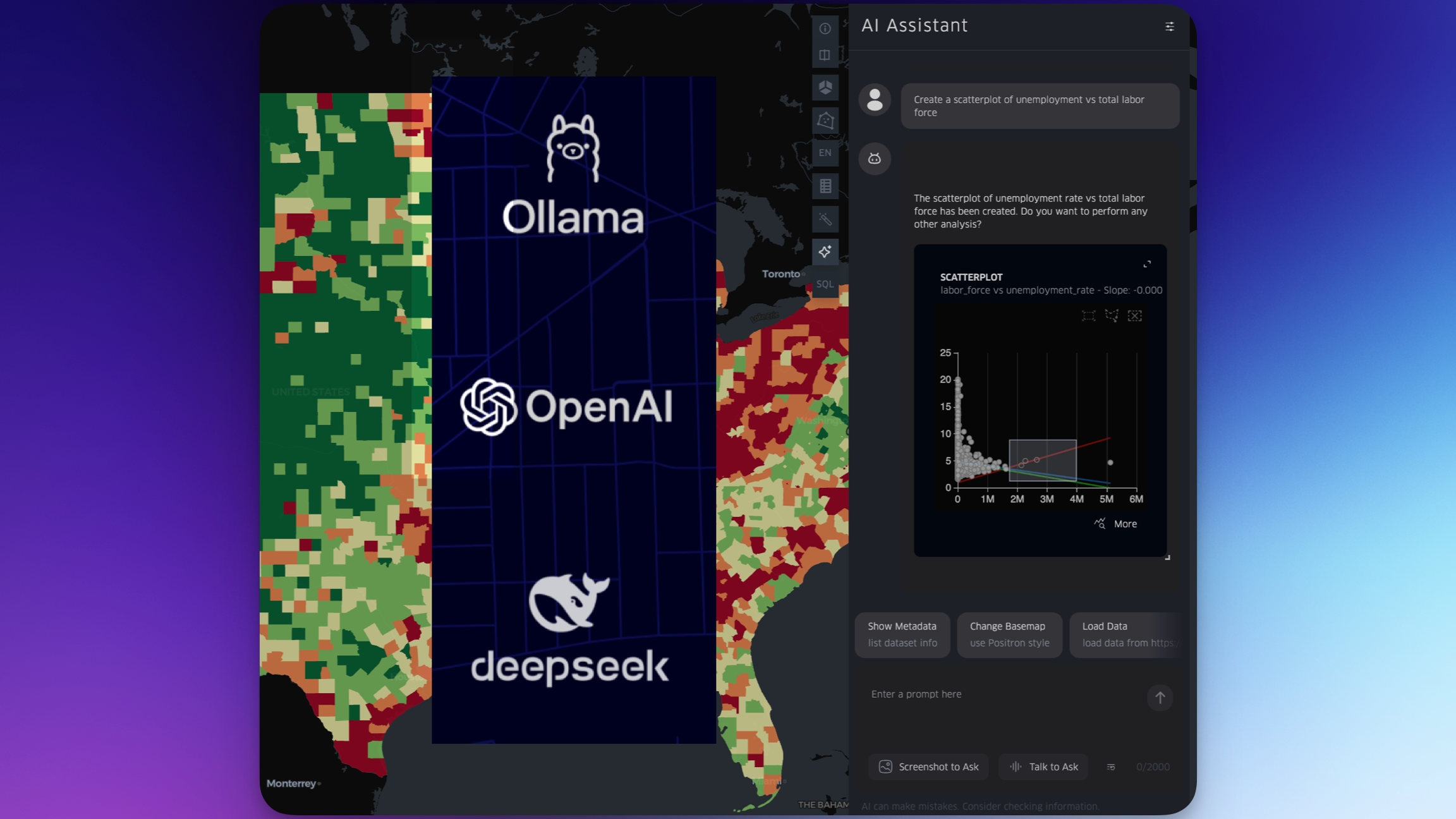
AI Assistant
Kepler’s AI assistant can edit the map, including filters, base map customization, and a variety of layer configurations. Accessible via text chat, voice chat, and screenshot. The assistant can also produce SQL from natural language, which can be passed to DuckDB.
Base Map Updates: MapLibre + Mapbox
Mapbox and MapLibre base maps are now simultaneously supported.
Color Scale Improvements
Custom color scale is now supported in categorial/ordinal fields, aggregate layers, and other layer components. In addition, custom breaks are now supported within the color scales.
Value Formatting
Formatting for numeric values (e.g. 10,000 can be formatted 10k, $10,000.00, etc; .42 can be formatted as 42%).
Animation Improvements
Includes various updates to the user interface for animation (for both time filters and the trip layer). You may also sync the layers (such as the trip layer) with filters, and conversely sync filters with the layer.
Legend Improvements
The legend is now both movable and resizable, supports the editing of legend values, and offers a scale for radius scaling.
Various Layer Improvements
A number of improvements to layers, including:
Zoom to layer button lets users center their viewport on the layer’s data
Point layer now supports geojson
Arc layer supports creation from h3
A vast number of other layer improvements
This release also includes a wide range of bug fixes and performance improvements, which can be viewed in the full change log.
Last updated
Was this helpful?